Treatment
There is no cure for Williams syndrome. Avoid taking extra calcium and vitamin D. Treat high levels of blood calcium, if present. Blood vessel narrowing can be a significant health problem and is treated based on its severity.
Physical therapy is helpful to patients with joint stiffness. Developmental and speech therapy can also help these children (for example, verbal strengths can help make up for other weaknesses). Other treatments are based on a patient’s symptoms.
It can help to have treatment coordinated by a geneticist who is experienced with Williams syndrome.
Support Groups
Williams Syndrome Foundation — www.wsf.org
Williams Syndrome Association — www.williams-syndrome.org
Prognosis (Expectations)
About 75% of those with Williams syndrome have some mental retardation.
Most patients will not live as long as normal, due to complications.
Most patients require full-time caregivers and often live in supervised group homes.
Complications
- Calcium deposits in the kidney and other kidney problems
- Death (in rare cases from anesthesia)
- Heart failure due to narrowed blood vessels
- Pain in the abdomen
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Many of the symptoms and signs of Williams syndrome may not be obvious at birth. Call your health care provider if your child has features similar to those of Williams syndrome. Seek genetic counseling if you have a family history of Williams syndrome.
Pictures & Images
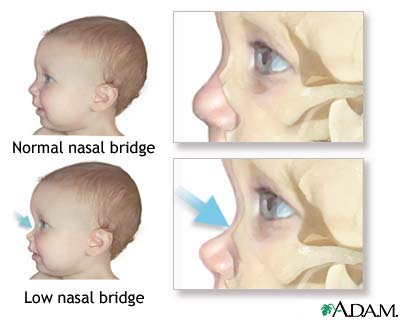
A low or absent nasal bridge can occur in association with infectious diseases or genetic diseases.
-
Williams syndrome:Overview, Causes
-
Williams syndrome:Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Williams syndrome:Treatment
Review Date : 10/14/2009
Reviewed By : Luc Jasmin, MD, PhD, Departments of Anatomy and Neurological Surgery, University of California, San Francisco, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.