Symptoms & Signs
Vitiligo is more noticeable in darker skinned people because of the contrast of white patches against dark skin.
There is a sudden or gradual appearance of flat areas of normal-feeling skin with complete pigment loss. Lesions appear as flat areas with no pigment and with a darker border. The edges are sharply defined but irregular.
Frequently affected areas are the face, elbows and knees, hands and feet, and genitalia.
Diagnosis & Tests
Examination is usually sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to rule out other causes of pigment loss. Your doctor may also perform blood tests to check the levels of thyroid or other hormones, and vitamin B12 levels.
Pictures & Images
Vitiligo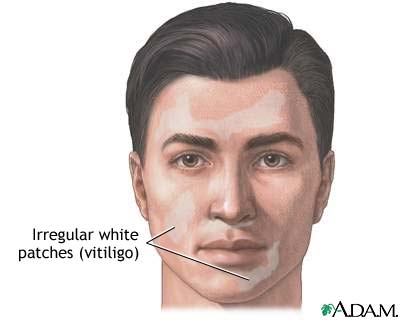
Vitiligo is a condition which involves complete loss of melanin, the primary skin pigment. The cause of vitiligo is unknown but it appears to be an acquired condition and may appear at any age. The resulting lesions are white in comparison to the surrounding skin. Vitiligo may occur in the same areas on both sides of the face or it may be patchy. The typical vitiligo lesion is flat and depigmented, but maintains the normal skin texture.
Review Date : 9/24/2008
Reviewed By : Benjamin Medoff, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Pulmonary and Critical Care Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
