Definition
Viral pneumonia is an inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the lungs caused by infection with a virus.
See also:
- Atypical pneumonia
- Influenza
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Respiratory syncytial virus
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung that affects 1 out of 100 people annually. Viral pneumonia is caused by one of several viruses, including influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus, herpes simplex virus, respiratory syncytial virus, hantavirus, and cytomegalovirus.
People at risk for more serious viral pneumonia typically have weakened immune systems. This includes young children, especially those with heart defects, and the elderly. The following also weaken the immune system and raise the risk for pneumonia:
- HIV
- Medications that suppress the immune system
- Organ transplant
Pictures & Images
Lungs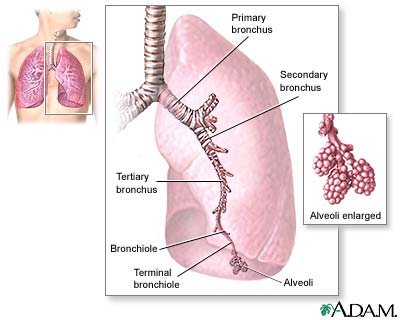
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Respiratory system
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
-
Viral pneumonia: Overview, Causes
-
Viral pneumonia: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Viral pneumonia: Treatment
Review Date : 9/24/2008
Reviewed By : Benjamin Medoff, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Pulmonary and Critical Care Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
