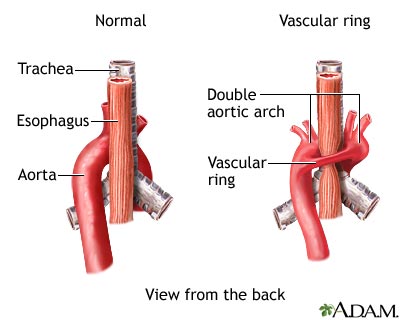
Treatment
Surgery is usually performed as soon as possible on children with symptoms. The goal of surgery is to split the vascular ring and relieve pressure on the surrounding structures. The surgery is not very invasive. The procedure is usually done through a small surgical cut in the left side of the chest between the ribs.
Changing the child’s diet may help relieve the digestive symptoms of vascular ring. The doctor will prescribe medications (such as antibiotics) to treat any respiratory tract infections, if they occur.
Children who don’t have symptoms may not need treatment, but should be carefully watched to make sure the condition doesn’t become worse.
Prognosis (Expectations)
How well the infant does depends on how much pressure the vascular ring is putting on the esophagus and trachea and how quickly the infant is diagnosed and treated.
Surgery works well in most cases and often relieves symptoms right away. Severe breathing problems may take months to go away. Some children may continue to have loud breathing, especially when they are very active or have respiratory infections.
Complications
Delaying surgery can lead to serious complications such as damage to the trachea and even death.
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Call your health care provider if your baby has symptoms of vascular ring. Getting diagnosed and treated quickly can prevent serious complications.
Pictures & Images
-
Vascular ring:Overview, Causes
-
Vascular ring: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Vascular ring:Treatment
Review Date : 6/1/2009
Reviewed By : Jeffrey Heit, MD, Internist with special emphasis on preventive health, fitness and nutrition, Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.