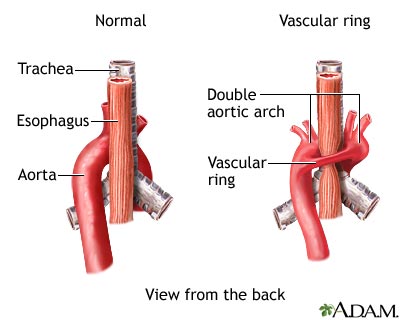
Symptoms & Signs
Some children with a vascular ring never develop symptoms. However, in most cases, symptoms are seen during infancy. Pressure on the windpipe (trachea) and esophagus can lead to breathing and digestive problems. The more the ring presses down, the more severe the symptoms will be.
Breathing problems may include:
- High-pitched cough
- Loud breathing (stridor)
- Repeated pneumonias or respiratory infections
- Respiratory distress
- Wheezing
Eating may make breathing symptoms worse.
Digestive symptoms are rare, but may include:
- Choking
- Difficulty eating solid foods
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Slow breast or bottle feeding
- Vomiting
Diagnosis & Tests
The doctor will listen to the baby’s breathing to rule out other breathing disorders such as asthma. Listening to the child’s heart through a stethoscope can help identify murmurs and other heart problems.
The following tests can help diagnose vascular ring:
- Chest x-ray
- Computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart
- Camera down the throat to examine the airways (bronchoscopy)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart
- Ultrasound examination (echocardiogram) of heart
- X-ray of blood vessels (angiography)
- X-ray of the esophagus using a special dye to better highlight the area (esophagram or barium swallow)
Pictures & Images
-
Vascular ring:Overview, Causes
-
Vascular ring: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Vascular ring:Treatment
Review Date : 6/1/2009
Reviewed By : Jeffrey Heit, MD, Internist with special emphasis on preventive health, fitness and nutrition, Philadelphia VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.