Treatment
The only treatment needed may simply involved routine exams and watching the cysts for growth and other changes.
Surgical excision (removal) may be chosen or possibly required if the cyst is causing symptoms. However, this can sometimes be a very involved surgery and is not recommended unless you are having significant symptoms.
Prognosis (Expectations)
The outcome is generally good. Frequently cysts remain small and require no treatment. When surgically removed, the cysts usually do not return.
Complications
There are usually no complications from the cysts themselves. A surgical excision procedure carries a small risk of complications depending on where the cyst is located in relation to other structures.
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Call your health care provider if a lump is felt inside the vagina or protruding from the vagina.
Pictures & Images
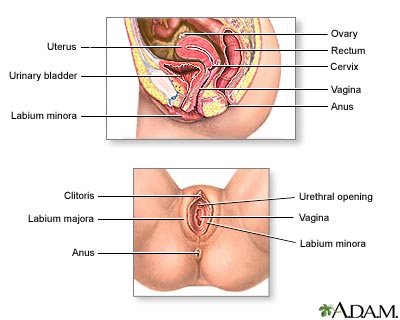
Female reproductive anatomy-
Vaginal cysts: Overview, Causes
-
Vaginal cysts: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Vaginal cysts:Treatment
Review Date : 11/1/2009
Reviewed By : Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington, School of Medicine; Susan Storck, MD, FACOG, Chief, Eastside Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Redmond, Washington; Clinical Teaching Faculty, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.