Definition
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) tumors that develop in the uterus (womb), a female reproductive organ.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Uterine fibroids are the most common pelvic tumor. As many as 1 in 5 women may have fibroids during their childbearing years (the time after starting menstruation for the first time and before menopause).
Fibroids usually affect women over age 30. They are rare in women under 20, and often shrink and cause no symptoms in women who have gone through menopause. They are more common in African Americans than Caucasians.
The cause of uterine fibroid tumors is unknown. However, fibroid growth seems to depend on the hormone estrogen. As long as a woman with fibroids is menstruating, a fibroid will probably continue to grow, usually slowly.
Fibroids can be so tiny that you need a microscope to see them. However, they can grow very large. They may fill the entire uterus, and may weigh several pounds. Although it is possible for just one fibroid to develop, usually there are more than one.
Fibroids are often described by their location in the uterus:
- Myometrial — in the muscle wall of the uterus
- Submucosal — just under the surface of the uterine lining
- Subserosal — just under the outside covering of the uterus
- Pendunculated — occurring on a long stalk on the outside of the uterus or inside the cavity of the uterus
Pictures & Images
Pelvic laparoscopy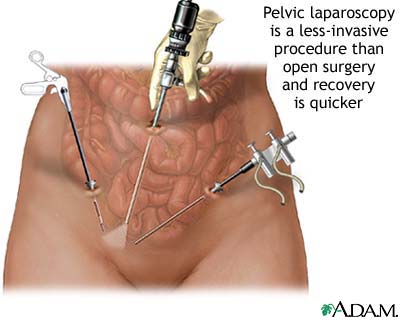 Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called “band-aid” surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accomodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called “band-aid” surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accomodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.

External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Fibroid tumors
Fibroid tumors may not need to be removed if they are not causing pain, bleeding excessively, or growing rapidly.
Uterus
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
-
Uterine fibroids: Overview, Causes
-
Uterine fibroids: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Uterine fibroids: Treatment
Review Date : 9/2/2009
Reviewed By : Susan Storck, MD, FACOG, Chief, Eastside Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Group Health Cooperative of Puget Sound, Redmond, Washington; Clinical Teaching Faculty, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
![]()
