Treatment
Your doctor must first decide whether you have a mild or simple bladder or kidney infection, or whether your infection is more serious.
MILD BLADDER AND KIDNEY INFECTIONS
Antibiotics taken by mouth are usually recommended because there is a risk that the infection can spread to the kidneys.
- For a simple bladder infection, you will take antibiotics for 3 days (women) or 7 – 14 days (men). For a bladder infection with complications such as pregnancy or diabetes, OR a mild kidney infection, you will usually take antibiotics for 7 – 14 days.
- It is important that you finish all the antibiotics, even if you feel better. People who do not finish their antibiotics may develop an infection that is harder to treat.
Commonly used antibiotics include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, amoxicillin, Augmentin, doxycycline, and fluoroquinolones. Your doctor will also want to know whether you could be pregnant.
Your doctor may also recommend drugs to relieve the burning pain and urgent need to urinate. Phenazopyridine hydrochloride (Pyridium) is the most common of this type of drug. You will still need to take antibiotics.
Everyone with a bladder or kidney infection should drink plenty of water.
Some women have repeat or recurrent bladder infections. Your doctor may suggest several different ways of treating these.
- Taking a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual contact may prevent these infections, which occur after sexual activity.
- Having a 3-day course of antibiotics at home to use for infections diagnosed based on your symptoms may work for some women.
- Some women may also try taking a single, daily dose of an antibiotic to prevent infections.
See also: Catheter-associated UTI
MORE SEVERE KIDNEY INFECTIONS
If you are very sick and cannot take medicines by mouth or drink enough fluids, you may be admitted to the hospital. You may also be admitted to the hospital if you:
- Are elderly
- Have kidney stones or changes in the anatomy of your urinary tract
- Have recently had urinary tract surgery
- Have cancer, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or other medical problems
- Are pregnant and have a fever or are otherwise ill
At the hospital, you will receive fluids and antibiotics through a vein.
Some people have urinary tract infections that keep coming back or that do not go away with treatment. Such infections are called chronic UTIs. If you have a chronic UTI, you may need antibiotics for a long period of time, perhaps as long as 6 months to 2 years, or stronger antibiotics may be prescribed.
If a structural (anatomical) problem is causing the infection, surgery may be recommended.
Prognosis (Expectations)
A urinary tract infection is uncomfortable, but treatment is usually successful. Symptoms of a bladder infection usually disappear within 24 – 48 hours after treatment begins. If you have a kidney infection, it may take 1 week or longer for your symptoms to go away.
Complications
- Life-threatening blood infection (sepsis) – risk is greater among the young, very old adults, and those whose bodies cannot fight infections (for example, due to HIV or cancer chemotherapy)
- Kidney damage or scarring
- Kidney infection
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of a UTI. Call right away if the following symptoms develop:
- Back or side pain
- Chills
- Fever
- Vomiting
These may be signs of a possible kidney infection.
Also call if you have already been diagnosed with a UTI and the symptoms come back shortly after treatment with antibiotics.
Prevention
Lifestyle changes may help prevent some UTIs.
After menopause, a woman may use estrogen cream in the vagina area to reduce the chance of further infections.
BATHING AND HYGIENE
- Choose sanitary pads instead of tampons, which some doctors believe make infections more likely. Change the pad each time you use the bathroom.
- Do not douche or use feminine hygiene sprays or powders. As a general rule, do not use any product containing perfumes in the genital area.
- Take showers instead of baths. Avoid bath oils.
- Keep your genital area clean. Clean your genital and anal areas before and after sexual activity.
- Urinate before and after sexual activity.
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom.
CLOTHING
- Avoid tight-fitting pants.
- Wear cotton-cloth underwear and pantyhose, and change both at least once a day.
DIET
- Drink plenty of fluids (2 to 4 quarts each day).
- Drink cranberry juice or use cranberry tablets, but NOT if you have a personal or family history of kidney stones.
- Do NOT drink fluids that irritate the bladder, such as alcohol and caffeine.
Pictures & Images
Bladder catheterization, female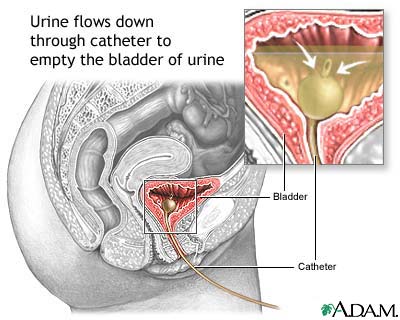
-
Urinary tract infection – adults: Overview, Causes
-
Urinary tract infection – adults: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Urinary tract infection – adults: Treatment
Review Date : 10/6/2009
Reviewed By : David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
![]()
