Treatment
Surgery to correct the blockage allows urine to flow normally. Open (invasive) surgery is usually performed in infants. Adults may be treated with less-invasive procedures. These procedures involve much smaller surgical cuts than open surgery, and may include:
- Endoscopic (retrograde) technique does not require a surgical cut on the skin. Instead, a small instrument is placed into the urethra and allows the surgeon to open the blockage from the inside.
- Percutaneous (antegrade) technique involves a small surgical cut on the side of the body between the ribs and the hip.
- Pyeloplasty removes scar tissue from the blocked area and connects the healthy part of the kidney to the healthy ureter.
Recently, laparoscopy has been used to treat UPJ obstruction in children and adults who have not had success with other procedures.
A tube called a stent may be placed to drain urine from the kidney until the patient heals. A nephrostomy tube, which is placed in the patient’s side to drain urine, may also be needed for a short time after the surgery. This type of tube may also used to treat severe infections before surgery.
Prognosis (Expectations)
Early diagnosis and treatment of UPJ obstruction may help preserve future kidney function. UPJ obstruction diagnosed before birth or early after birth may actually improve on its own.
Most patients do well with no long-term consequences. Significant kidney damage may occur in those who are diagnosed later in life. Current treatment options provide good long-term outcomes. Pyeloplasty provides the greatest long-term success.
In severe cases, rapidly taking pressure off the kidney (kidney decompression) immediately following birth may greatly improve kidney function.
Complications
Permanent loss of kidney function (kidney failure) is a possible complication of untreated UPJ obstruction. Even after treatment, the affected kidney may be at increased risk for infection or kidney stones.
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Call your health care provider if your infant has bloody urine, fever, a lump in the abdomen or if the baby seems to have back pain or pain in the flanks (the area towards the sides of the body between the ribs and the pelvis).
Pictures & Images
Kidney anatomy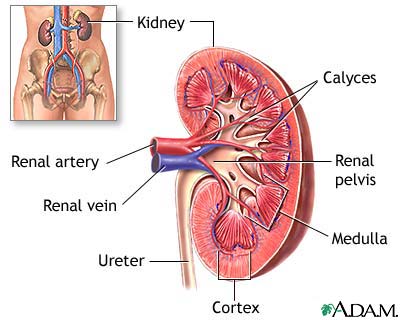
-
UPJ obstruction: Overview, Causes
-
UPJ obstruction: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
UPJ obstruction: Treatment
Review Date : 2/9/2009
Reviewed By : Linda Vorvick, MD, Family Physician, Seattle Site Coordinator, Lecturer, Pathophysiology, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, University of Washington School of Medicine; Louis S. Liou, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor of Urology, Department of Surgery, Boston University School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
