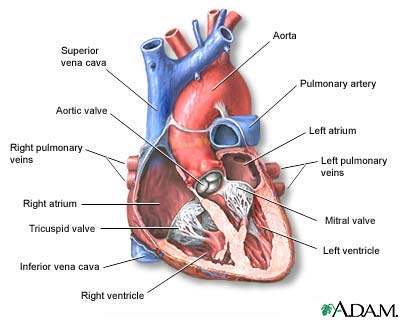
Symptoms & Signs
Most patients have no symptoms until the aneurysm begins to leak or expand. Chest or back pain may mean sudden widening or leakage of the aneurysm.
Diagnosis & Tests
The physical examination is often normal. Most nonleaking thoracic aortic aneurysms are detected by tests — usually a chest x-ray or a chest CT scan — run for other reasons. A chest x-ray and chest CT scan show if the aorta is enlarged. A chest CT scan shows the size of the aorta and the exact location of the aneurysm.
Pictures & Images
An aortogram (a special set of x-ray images made when dye is injected into the aorta) can identify the aneurysm and any branches of the aorta that may be involved.
-
Thoracic aortic aneurysm: Overview, Causes
-
Thoracic aortic aneurysm: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Thoracic aortic aneurysm: Treatment
Review Date : 5/6/2009
Reviewed By : Robert A. Cowles, MD, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.