Treatment
Surgery to repair tetralogy of Fallot is done when the infant is very young. Sometimes more than one surgery is needed. When more than one surgery is used, the first surgery is done to help increase blood flow to the lungs.
Surgery to correct the problem may be done at a later time. Often only one corrective surgery is performed in the first few months of life. Corrective surgery is done to widen part of the narrowed pulmonary tract and close the ventricular septal defect.
Prognosis (Expectations)
Most cases can be corrected with surgery. Babies who have surgery usually do well. Ninety percent survive to adulthood and live active, healthy, and productive lives. Without surgery, death usually occurs by the time the person reaches age 20.
Patients who have continued, severe leakiness of the pulmonary valve may need to have the valve replaced.
Regular follow-up with a cardiologist to monitor for life-threatening arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) is recommended.
Complications
- Delayed growth and development
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Seizures during periods when there is not enough oxygen
- Death
Calling Your Health Care Provider
Call your health care provider if new unexplained symptoms develop or the patient is having an episode of cyanosis (blue skin).
If a child with tetralogy of Fallot becomes blue, immediately place the child on his or her side or back and put the knees up to the chest. Calm the baby and seek medical attention immediately.
Pictures & Images
Heart, section through the middle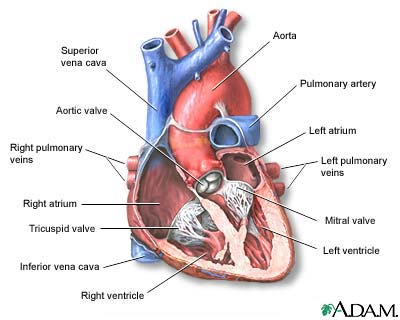
-
Tetralogy of Fallot: Overview, Causes
-
Tetralogy of Fallot: Symptoms & Signs Diagnosis & Tests
-
Tetralogy of Fallot: Treatment
Review Date : 12/21/2009
Reviewed By : Kurt R. Schumacher, MD, Pediatric Cardiology, University of Michigan Congenital Heart Center, Ann Arbor, MI. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
