Symptoms & Signs
There may be no symptoms. Symptoms that may occur can include:
- Discomfort or pain in the testicle, or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- Dull ache in the back or lower abdomen
- Enlargement of a testicle or a change in the way it feels
- Excess development of breast tissue (gynecomastia), however, this can occur normally in adolescent boys who do not have testicular cancer
- Lump or swelling in either testicle
Symptoms in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, abdomen, pelvis, back, or brain, may also occur if the cancer has spread.
Diagnosis & Tests
A physical examination typically reveals a firm lump (mass) in one of the testicles. When the health care provider holds a flashlight up to the scrotum, the light does not pass through the lump.
Other tests include:
- Abdominal and pelvic CT scan
- Blood tests for tumor markers: alpha fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta HCG), and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Chest x-ray
- Ultrasound of the scrotum
A biopsy of the tissue is usually done after the entire testicle is surgically removed.
Pictures & Images
Male reproductive anatomy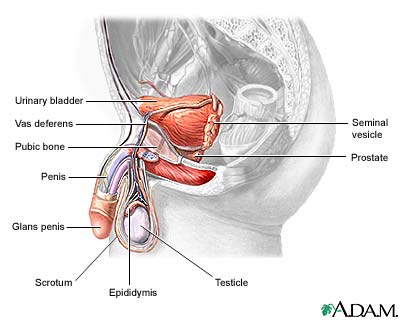
-
Testicular cancer: Overview, Causes
-
Testicular cancer: Symptoms & Signs Diagnosis & Tests
-
Testicular cancer: Treatment
Review Date : 4/5/2009
Reviewed By : David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; Yi-Bin Chen, MD, Leukemia/Bone Marrow Transplant Program, Massachusetts General Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
