Symptoms & Signs
Neurofibromatosis causes unchecked growth of tissue along the nerves. This can put pressure on affected nerves and cause pain, severe nerve damage, and loss of function in the area served by the nerve. Problems with sensation or movement can occur, depending on the nerves affected.
The condition can be very different from person to person, even among people in the same family who have the NF1 gene.
The “coffee-with-milk” (café-au-lait) spots are the hallmark symptom of neurofibromatosis. Although many healthy people have 1 or 2 small café-au-lait spots, adults with 6 or more spots greater than 1.5 cm in diameter are likely to have neurofibromatosis. In most people with the condition, these spots may be the only symptom.
Other symptoms may include:
- Blindness
- Convulsions
- Freckles in the underarm or groin
- Large, soft tumors called plexiform neurofibromas, which may have a dark color and may spread under the surface of the skin
- Pain (from affected peripheral nerves)
- Small, rubbery tumors of the skin called nodular neurofibromas
Diagnosis & Tests
Diagnosis is made by a doctor familiar with NF1, including a neurologist, geneticist, dermatologist, or developmental pediatrician. The diagnosis will usually be made based on the unique symptoms and signs of neurofibromatosis.
Signs include:
- Colored, raised spots (Lisch nodules) on the colored part (iris) of the eye
- Fracture of the long bones of the leg in early childhood
- Freckling in the armpits, groin, or underneath the breast in women
- Large tumors under the skin (plexiform neurofibromas), which can affect the appearance and put pressure on nearby nerves or organs
- Many soft tumors on the skin or deeper in the body
- Mild cognitive impairment, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, learning disorders
- Soft nodules under the skin
Tests may include:
- Eye exam by an ophthalmologist familiar with NF1
- Genetic tests to find a change (mutation) in the neurofibromin gene
- MRI of the affected site
- Other specific tests for complications
Pictures & Images
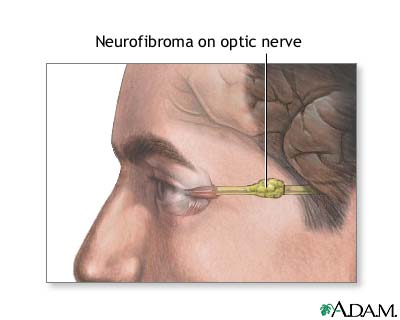
Neurofibroma is a tumor or growth located along a nerve or nervous tissue. It is an inherited disorder. If left unchecked, a neurofibroma can cause severe nerve damage leading to loss of function to the area stimulated by that nerve.
-
Neurofibromatosis-1: Overview, Cause
-
Neurofibromatosis-1: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Neurofibromatosis-1: Treatment
Review Date : 8/7/2008
Reviewed By : Diana Chambers, MD, EdD, Certified Genetics Counselor (ABMG), Charter Member of the ABGC, Univresity of Tennessee, Memphis, TN. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
