You do not want to fall into the condition of unemployment and need to find a job. However, when you have had your favorite job already, there will be many coming problems which can cause tress and depression. That is the reason here listing some occupations physical toll – or on-the-job pains, as we know: persistent aching, throbbing or tingling in the hand, wrist, elbow, shoulder or neck.
Back pain is the most common work-related injury and one of the biggest causes of back pain is repetitive motion. So the tip is to reduce repetitive motion. In some cases, you can get pain relief simply by taking more breaks or by alternating tasks so that you are not performing the same motion over and over for hours.
Define the back pain cause
Sitting in an office chair for prolonged periods of time can definitely cause low back pain or worsen an existing back or neck problem. The main reason behind this is that sitting, in an office chair or in general, is a static posture that increases stress in the back, neck, shoulders, arms and legs, and in particular, can add large amounts of pressure to the back muscles and spinal discs.
When sitting in an office chair for a long period, the natural tendency for most people is to slouch over or slouch down in the chair, and this posture can overstretch the spinal ligaments and strain the discs and surrounding structures in the spine. Over time, incorrect sitting posture can damage spinal structures and contribute to or worsen back and neck pain.
Guidelines for Office Chair Setup
To maximize back support and maintain good posture while sitting, the best choice is the use of an ergonomic office chair. However, simply owning an ergonomic office chair is not enough – it is also necessary to adjust the office chair to the proportions of the individual’s body to improve comfort and reduce aggravation to the low back and neck.
The first step in setting up an office chair is to establish the desired height of the individual’s desk or workstation. This decision is determined primarily by the type of work to be done and by the height of the person using the office chair. The height of the desk or workstation itself can vary greatly and will require different positioning of the office chair, or a different type of ergonomic chair altogether.
Once the workstation has been situated, then the user can adjust the office chair according to his or her physical proportions. Here are the most important guidelines – distilled into a quick checklist – to help make sure that the office chair and work area are as comfortable as possible and will cause the least amount of stress to the spine:
- Elbow measure
First, begin by sitting comfortably as close as possible to your desk so that your upper arms are parallel to your spine. Rest your hands on your work surface (e.g. desktop, computer keyboard). If your elbows are not at a 90-degree angle, adjust your office chair height either up or down. - Thigh measure
Check that you can easily slide your fingers under your thigh at the leading edge of the office chair. If it is too tight, you need to prop your feet up with an adjustable footrest. If you are unusually tall and there is more than a finger width between your thigh and the chair, you need to raise the desk or work surface so that you can raise the height of your office chair. - Calf measure
With your bottom pushed against the chair back, try to pass your clenched fist between the back of your calf and the front of your office chair. If you can’t do that easily, then the office chair is too deep. You will need to adjust the backrest forward, insert a low back support (such as a lumbar support cushion, a pillow or rolled up towel), or get a new office chair. - Low back support
Your bottom should be pressed against the back of your chair, and there should be a cushion that causes your lower back to arch slightly so that you don’t slump forward or slouch down in the chair as you tire over time. This low back support in the office chair is essential to minimize the load (strain) on your back. Never slump or slouch forward in the office chair, as that places extra stress on the structures in the low back, and in particular, on the lumbar discs. - Resting eye level
Close your eyes while sitting comfortably with your head facing forward. Slowly open your eyes. Your gaze should be aimed at the center of your computer screen. If your computer screen is higher or lower than your gaze, you need to either raise or lower it to reduce neck strain. - Armrest
Adjust the armrest of the office chair so that it just slightly lifts your arms at the shoulders. Use of an armrest on your office chair is important to take some of the strain off your neck and shoulders, and it should make you less likely to slouch forward in your chair.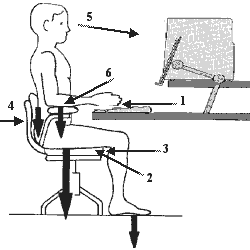
No matter how comfortable one is in an office chair, prolonged static posture is not good for the back and is a common contributor to back problems and muscle strain. To avoid keeping the back in one position for a long period, remember to stand, stretch and walk for at least a minute or two every half hour. Even a quick stretch or some minimal movement – such as walking to the water cooler or bathroom – will help.
A twenty minute walk will help even more, promoting healthy blood flow that brings important nutrients to all the spinal structures. In general, moving about and stretching on a regular basis throughout the day will help keep the joints, ligaments, muscles and tendons loose, which in turn promotes an overall feeling of comfort, relaxation and ability to focus productively. Hope that after reading these information, you will be able to get rid of on-the-job pain in general, and back pain in particular.
