Alternate Names : Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Definition
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a potentially life-threatening blood disorder in a fetus or newborn infant. This article provides a general overview. For more detailed information see the specific disorder:
- ABO incompatibility
- Rh incompatibility
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Erythroblastosis fetalis develops in an unborn infant when the mother and baby have different blood types. The mother produces substances called antibodies that attack the developing baby’s red blood cells.
The most common form of erythroblastosis fetalis is ABO incompatibility, which can vary in severity.
The less common form is called Rh incompatibility, which can cause very severe anemia in the baby.
Pictures & Images
Intrauterine transfusion
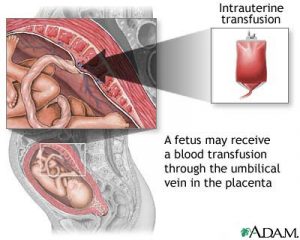
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a condition manifested by anemia that develops in an unborn infant when maternal antibodies, usually caused by Rh incompatibility between the mother’s blood type and that of the fetus, attack the red blood cells of the fetus. An intrauterine transfusion of blood may be indicated.
Antibodies

Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
-
Erythroblastosis fetalis : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Erythroblastosis fetalis : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Erythroblastosis fetalis : Treatment



Review Date : 9/3/2008
Reviewed By : D. Scott Smith, M.D., MSc, DTM&H, Chief of Infectious Disease & Geographic Medicine, Kaiser Redwood City, CA & Adjunct Assistant Professor, Stanford University.� Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only — they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2010 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
