Alternate Names : Hydatidosis, Hydatid disease, Hydatid cyst disease
Definition
Echinococcus is an infection caused by the Echinococcus granulosus or Echinococcus multilocularis worm.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Echinococcus is common in:
- Africa
- Central Asia
- Southern South America
- The Mediterranean
- The Middle East
In the United States, the disease is very rare. However, it has been reported in California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah.
Humans become infected when they swallow eggs in contaminated food. The infection is carried to the liver, where cysts form. Cysts can also form in the:
- Brain
- Bones
- Kidney
- Lungs
- Skeletal muscles
- Spleen
Risk factors include being exposed to:
- Cattle
- Deer
- Feces of dogs, wolves, or coyotes
- Pigs
- Sheep
Pictures & Images
Liver echinococcus – CT scan
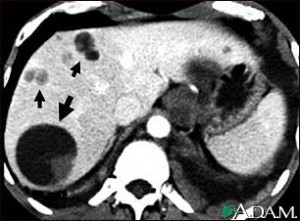 This upper abdominal CT scan shows multiple cysts in the liver, caused by dog tapeworm (echinococcus). Note the large circular cyst (seen on the left side of the screen) and multiple smaller cysts throughout the liver.
This upper abdominal CT scan shows multiple cysts in the liver, caused by dog tapeworm (echinococcus). Note the large circular cyst (seen on the left side of the screen) and multiple smaller cysts throughout the liver.
Antibodies

Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
-
Echinococcus : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Echinococcus : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Echinococcus : Treatment



Review Date : 9/3/2008
Reviewed By : D. Scott Smith, M.D., MSc, DTM&H, Chief of Infectious Disease & Geographic Medicine, Kaiser Redwood City, CA & Adjunct Assistant Professor, Stanford University.� Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only — they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2010 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
