Alternate Names : Ebola virus infection, Viral hemorrhagic fever
Definition
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a severe and often deadly illness that can occur in humans and in primates (monkeys, gorillas).
Ebola hemorrhagic fever has made worldwide news because of its destructive potential.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Ebola hemorrhagic fever (Ebola fever) is caused by a virus belonging to the family called Filoviridae. Scientists have identified four types of the Ebola virus. Three have been reported to cause disease in humans: Ebola-Zaire virus, Ebola-Sudan virus, and Ebola-Ivory Coast virus. The human disease has so far been limited to parts of Africa.
A very small number of people in the United States who were infected with the fourth type of the virus, known as Ebola Reston, did not develop any signs of disease.
The disease can be passed to humans from infected animals and animal materials. Ebola can also be spread between humans by close contact with infected bodily fluids or through infected needles in the hospital.
Pictures & Images
Ebola virus
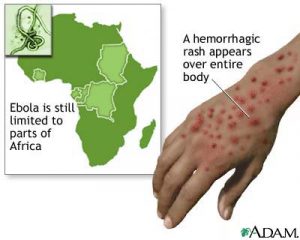 Ebola is a virus-caused disease limited to parts of Africa. Within a week, a raised rash, often hemorrhagic (bleeding), spreads over the body. Bleeding from the mucous membranes is typical causing apparent bleeding from the mouth, nose, eyes and rectum.
Ebola is a virus-caused disease limited to parts of Africa. Within a week, a raised rash, often hemorrhagic (bleeding), spreads over the body. Bleeding from the mucous membranes is typical causing apparent bleeding from the mouth, nose, eyes and rectum.
Antibodies

Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
-
Ebola hemorrhagic fever : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Ebola hemorrhagic fever : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Ebola hemorrhagic fever : Treatment



Review Date : 9/3/2008
Reviewed By : D. Scott Smith, M.D., MSc, DTM&H, Chief of Infectious Disease & Geographic Medicine, Kaiser Redwood City, CA & Adjunct Assistant Professor, Stanford University.� Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only — they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2010 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
