Alternate Names : Middle ear infection – chronic, Otitis media – chronic, Chronic otitis media, Chronic ear infection
Definition
Chronic ear infection is inflammation or infection of the middle ear that persists or keeps coming back, and causes long-term or permanent damage to the ear.
See also: Acute ear infection
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
For each ear, a eustachian tube runs from the middle ear to the back of the throat. This tube drains fluid that is normally made in the middle ear. If the eustachian tube becomes blocked, fluid can build up. When this happens, germs such as bacteria and viruses can multiply and cause an infection. This is called an acute ear infection (acute otitis media).
A chronic ear infection occurs when fluid or an infection behind the eardrum does not go away. A chronic ear infection may be caused by an acute ear infection that does not clear completely, or repeated ear infections. Fluid in the middle ear may become very thick. Sometimes, the eardrum (tympanic membrane) may stick to the bones in the middle ear.
A chronic ear infection may cause permanent changes to the ear and nearby bones, including:
- Infection in the mastoid bone behind the ear (mastoiditis)
- Ongoing drainage from a hole in the eardrum that does not heal, or after the ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes) are inserted
- Cyst of the middle ear (cholesteatoma)
- Hardening of the tissue in the middle ear (tympanosclerosis)
- Damage to, or wearing away of the bones of the middle ear, which help with hearing
“Suppurative chronic otitis” is a phrase doctors use to describe an eardrum that keeps rupturing, draining, or swelling in the middle ear or mastoid area and does not go away.
Ear infections are more common in children because their Eustachian tubes are shorter, narrower, and more horizontal than in adults. Chronic ear infections are much less common than acute ear infections.
Pictures & Images
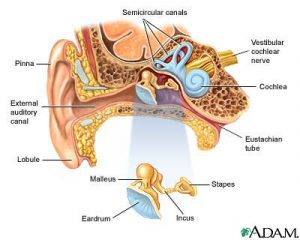
Ear anatomy
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the three tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)

Otitis media is an inflammation and/or infection of the middle ear. Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Middle ear infection

A middle ear infection is also known as otitis media. It is one of the most common of childhood infections. With this illness, the middle ear becomes red, swollen, and inflamed because of bacteria trapped in the eustachian tube.
Ear tube insertion – series
Normal anatomy

The eardrum (tympanic membrane) separates the ear canal from the middle ear.
-
Ear infection – chronic : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Ear infection – chronic : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Ear infection – chronic : Treatment



Review Date : 6/2/2009
Reviewed By : Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only — they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2010 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.