Alternate Names : Renal tubular acidosis – distal, Renal tubular acidosis type I, Type I RTA, RTA – distal, Classical RTA
Definition
Distal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys don’t remove acid properly into the urine, leaving the blood too acidic (called acidosis).
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Your kidneys normally regulate your body’s pH by removing acids from the blood and discarding them into the urine.
Distal renal tubular acidosis (Type I RTA) is caused by a defect in the kidney tubes that causes acid to build up in the bloodstream.
Type I RTA is caused by a variety of conditions, including:
- Amyloidosis
- Fabry disease
- Sickle cell disease
- Sjogren syndrome
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Wilson disease
- Use of certain drugs such as amphotericin B, lithium, and analgesics
Pictures & Images
Kidney anatomy
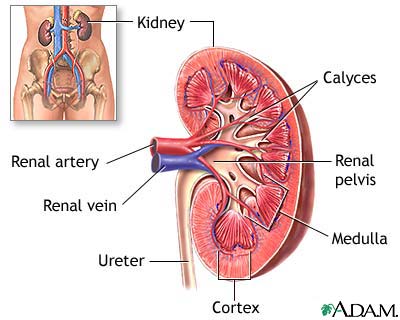 The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and stimulating�red blood cell production.
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and stimulating�red blood cell production.
Kidney – blood and urine flow

This is the typical appearance of the blood vessels (vasculature) and urine flow pattern in the kidney. The blood vessels are shown in red and the urine flow pattern in yellow.
-
Distal renal tubular acidosis : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Distal renal tubular acidosis : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Distal renal tubular acidosis : Treatment



Review Date : 11/30/2009
Reviewed By : David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; Herbert Y. Lin, MD, PHD, Nephrologist, Massachusetts General Hospital; Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only — they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2010 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
