Alternate Names : Hypoxic encephalopathy
Definition
Cerebral hypoxia technically means a lack of oxygen supply to the outer part of the brain, an area called the cerebral hemisphere. However, the term is more typically used to refer to a lack of oxygen supply to the entire brain.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
There are many causes of cerebral hypoxia. These include, but are not limited to:
- Asphyxiation caused by smoke inhalation
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Cardiac arrest (when the heart stops pumping)
- Choking
- Complications of general anesthesia
- Compression of the windpipe (trachea)
- Diseases that cause a loss of movement (paralysis) of the breathing muscles
- Drowning
- Drug overdose
- High altitudes
- Injuries before, during, or soon after, birth (See: Cerebral palsy)
- Strangulation
- Stroke
- Very low blood pressure
Brain cells are extremely sensitive to oxygen deprivation. Some brain cells actually start dying less than 5 minutes after their oxygen supply disappears. As a result, brain hypoxia can rapidly cause death or severe brain damage.
Pictures & Images
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system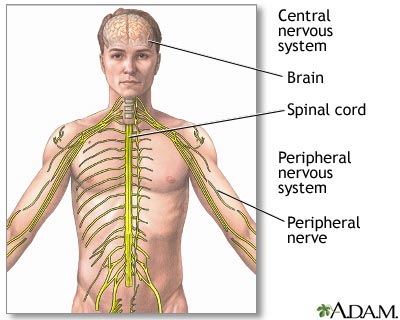
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
-
Cerebral hypoxia : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Cerebral hypoxia : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Cerebral hypoxia : Treatment



Review Date : 9/22/2008
Reviewed By : Daniel B. Hoch, PhD, MD, Assistant Professor of Neurology, Harvard Medical School, Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
