Alternate Names : Tamponade, Pericardial tamponade
Definition
Cardiac tamponade is the compression of the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) and the pericardium (the outer covering sac of the heart).
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
In this condition, blood or fluid collects within the pericardium. This prevents the ventricles from expanding fully. They cannot fill enough or pump blood.
Cardiac tamponade can occur due to:
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm (thoracic)
- End-stage lung cancer
- Heart attack (acute MI)
- Heart surgery
- Pericarditis caused by bacterial or viral infections
- Wounds to the heart
Other potential causes include:
- Heart tumors
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney failure
- Radiation therapy to the chest
- Recent invasive heart procedures
- Recent open heart surgery
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Cardiac tamponade occurs in approximately 2 out of 10,000 people.
Pictures & Images
Heart, front view
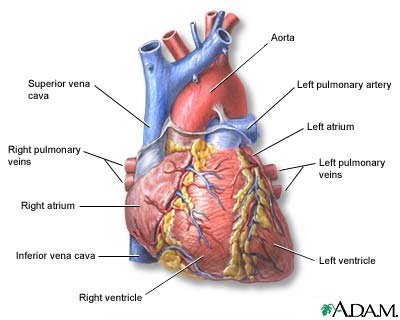 The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Pericardium

The pericardium is a thin double-layered sac which encloses the heart. Fluid is contained within the layers and lubricates the constantly rubbing surfaces.
Cardiac tamponade

Cardiac tamponade is a condition involving compression of the heart caused by blood or fluid accumulation in the space between the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) and the pericardium (the outer covering sac of the heart). Blood or fluid collects within the pericardium. This prevents the ventricles from expanding fully, so they cannot adequately fill or pump blood. Cardiac tamponade is an emergency condition that requires hospitalization.
-
Cardiac tamponade : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Cardiac tamponade : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Cardiac tamponade : Treatment



Review Date : 5/15/2008
Reviewed By : Robert A. Cowles, MD, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
