Alternate Names : Alcohol dependence, Alcohol abuse
Definition
Alcoholism is drinking alcoholic beverages at a level that interferes with physical health, mental health, and social, family, or job responsibilities.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Alcoholism is a type of drug addiction. There is both physical and mental dependence on alcohol.
Alcoholism is divided into 2 categories: dependence and abuse. People who are dependent on alcohol spend a great deal of time drinking alcohol, and getting it.
Physical dependence involves:
* A need for increasing amounts of alcohol to get drunk or achieve the desired effect (tolerance)
* Alcohol-related illnesses
* Memory lapses (blackouts) after drinking episodes
* Withdrawal symptoms when alcohol use is stopped
The most severe drinking behavior includes long drinking binges that lead to mental or physical problems. Some people are able to gain control over their dependence in earlier phases before they totally lose control. But no one knows which heavy drinkers will be able to regain control and which will not.
There is no known common cause of alcoholism. However, several factors may play a role in its development. A person who has an alcoholic parent is more likely to become an alcoholic than a person without alcoholism in the immediate family.
Research suggests that certain genes may increase the risk of alcoholism, but which genes or how they work is not known.
Psychological factors may include:
* A need for anxiety relief
* Conflict in relationships
* Depression
* Low self-esteem
Social factors include:
* Ease of getting alcohol
* Peer pressure
* Social acceptance of alcohol use
* Stressful lifestyle
The incidence of alcohol intake and related problems is rising. Data indicate that about 15% of people in the United States are problem drinkers, and about 5% to 10% of male drinkers and 3% to 5% of female drinkers could be diagnosed as alcohol dependent.
Pictures & Images
Liver cirrhosis, CT scan
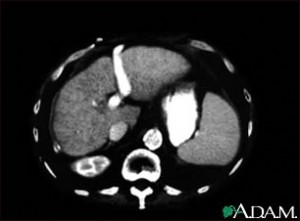 A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing cirrhosis of the liver.
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing cirrhosis of the liver.
Liver fattening, CT scan

A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a fatty liver (steatosis of the liver). Note the liver enlargement and dark color compared with the spleen (gray body in lower right).
Liver with disproportional fattening, CT scan

A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing disproportional steatosis (fattening) of the liver.
Alcoholism

Alcoholism is a chronic illness marked by dependence on alcohol consumption that interferes with physical or mental health, and social, family or job responsibilities. This addiction can lead to liver, circulatory and neurological problems. Pregnant women who drink alcohol in any amount may harm the fetus.
Alcoholism

Alcoholism is a chronic illness marked by dependence on alcohol consumption that interferes with physical or mental health, and social, family or job responsibilities. This addiction can lead to liver, circulatory and neurological problems. Pregnant women who drink alcohol in any amount may harm the fetus.
Alcohol and diet

Alcohol is considered a macronutrient in that it provides energy (about 7 calories per gram). The equivalent of a 1-ounce shot of liquor is approximately 80 to 90 calories.
Liver anatomy

The liver serves a wide variety of body functions, including detoxifying blood and producing bile that aids in digestion.
Alcoholism: Overview, Causes
Alcoholism: Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
Alcoholism: Treatment
Reviewed By : George F. Longstreth, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Kaiser Permanente Medical Care Program, San Diego, California. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
