Alternate Names : Inflammation – bronchi, Acute bronchitis
Definition
Bronchitis is inflammation of the main air passages to the lungs. Bronchitis may be short-lived (acute) or chronic, meaning that it lasts a long time and often recurs.
See also: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Acute bronchitis generally follows a viral respiratory infection. At first, it affects your nose, sinuses, and throat and then spreads to the lungs. Sometimes, you may get another (secondary) bacterial infection in the airways.This means that bacteria infect the airways, in addition to the virus.
People at risk for acute bronchitis include:
- The elderly, infants, and young children
- Persons with heart or lung disease
- Smokers
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition. People have a cough that produces excessive mucus. To be diagnosed with chronic bronchitis, you must have a cough with mucus most days of the month for at least 3 months.
Chronic bronchitis is one type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD for short. (Emphysema is another type of COPD.)
The following things can make bronchitis worse:
- Air pollution
- Allergies
- Certain occupations (such as coal mining, textile manufacturing, or grain handling)
- Infections
Pictures & Images
Lungs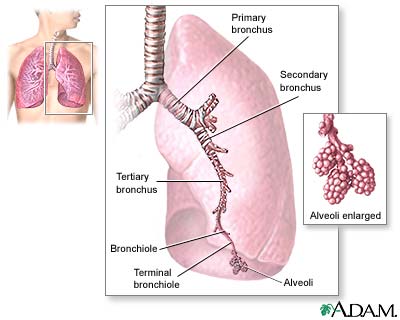
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Bronchitis

Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchi, the main air passages to the lungs, it generally follows a viral respiratory infection. Symptoms include; coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing and fatigue.
Lung anatomy

When air is inhaled through the nose or mouth, it travels down the trachea to the bronchus, where it first enters the lung. From the bronchus, air goes through the bronchi, into the even smaller bronchioles and lastly into the alveoli.
Bronchitis and normal condition in tertiary bronchus

Bronchitis is an inflammation of the air passages in the lungs. The condition occurs over a long period and recurs over several years. Symptoms include excessive bronchial mucus with a cough producing sputum. Cigarette smoking (active and passive exposure) is the chief cause of this disease, with air pollution, infection, familial factors, and allergies as exacerbating factors.
Cause of acute bronchitis

Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the part of the respiratory system that leads into the lungs. Acute bronchitis has a sudden onset and usually appears after a respiratory infection, such as a cold, and can be caused by either a virus or bacteria. The infection inflames the bronchial tubes, which causes symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, wheezing, and the production of thick yellow mucus. If acute bronchitis occurs because of a bacterial infection antibiotics are given for the treatment. Otherwise if the infection is viral medications can only be given to alleviate the symptoms. Although acute bronchitis is relatively common, some people are more prone to it than others.
Cause of chronic bronchitis

Chronic bronchitis is most frequently caused by long term irritation of the bronchial tubes. Bronchitis is considered “chronic” if symptoms continue for three months or longer. Bronchitis caused by allergies can also be classified as chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is caused most often by exposure to airborne pollutants such as cigarette smoke, excessive dust in the air, or chemicals. The bronchial lining becomes inflamed and the constant exposure to such pollutants begins to cause damage in the bronchioles (the smaller airways in the lungs). Symptoms of chronic bronchitis include shortness of breath or wheezing, chest pain, and chronic productive cough.
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder)

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to chronic lung disorders that result in blocked air flow in the lungs. The two main COPD disorders are emphysema and chronic bronchitis, the most common causes of respiratory failure. Emphysema occurs when the walls between the lung’s air sacs become weakened and collapse. Damage from COPD is usually permanent and irreversible.
-
Bronchitis : Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
-
Bronchitis : Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Bronchitis : Treatment



Review Date : 9/24/2008
Reviewed By : Benjamin Medoff, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Pulmonary and Critical Care Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
