Definition
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a heart condition in which there is an extra electrical pathway (circuit) in the heart. The condition can lead to episodes of rapid heart rate (tachycardia).
Wolff-Parkinson-White is one of the most common causes of fast heart rate disorders in infants and children.
Overview, Causes, & Risk Factors
Normally, electrical signals in the heart go through a pathway that helps the heart beat regularly. The wiring of the heart prevents extra beats from occurring and keeps the next beat from happening too soon.
In people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, there is an extra, or accessory, pathway that may cause a very rapid heart rate. This is called supraventricular tachycardia.
Pictures & Images
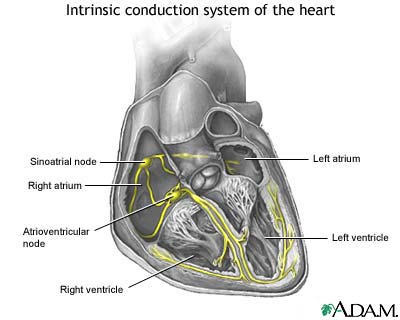
Conduction system of the heart
The intrinsic conduction system sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart by generating impulses which stimulate the heart to contract.

Atrioventricular block, ECG tracing
This picture shows an ECG (electrocardiogram, EKG) of a person with an abnormal rhythm (arrhythmia) called an atrioventricular (AV) block. P waves show that the top of the heart received electrical activity. Each P wave is usually followed by the tall (QRS) waves. QRS waves reflect the electrical activity that causes the heart to contract. When a P wave is present and not followed by a QRS wave (and heart contraction), there is an atrioventricular block, and a very slow pulse (bradycardia).

ECG
The electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is used extensively in the diagnosis of heart disease, from congenital heart disease in infants to myocardial infarction and myocarditis in adults. Several different types of electrocardiogram exist.

Normal heart rhythm
An electrocardiogram (ECG) test measures the electrical activity of the heart. A normal resting heart rate is 60 – 100 beats per minute.

Heart, section through the middleThe interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.

Heart, front view
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.

Bradycardia
Bradycardia heart rhythms are characterized by a slowness of the heartbeat, usually at a rate under 60 beats per minute (normal resting rate is 60 – 100 beats per minute).
-
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome:Overview, Causes
-
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome:Symptoms & Signs, Diagnosis & Tests
-
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome:Treatment
-
Review Date : 4/23/2009
Reviewed By : Steven Kang, MD, Division of Cardiac Pacing and Electrophysiology, East Bay Arrhythmia, Cardiovascular Consultants Medical Group, Oakland, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.